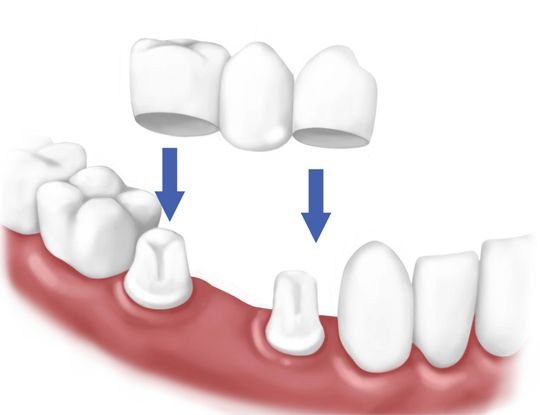
A crown is a cap that is placed over a tooth and held in place by dental adhesive or cement. Crowns are used for several reasons:
Crowns can be made from a variety of materials. They can be made from plastic, ceramic or metal alloys. A combination of metal and ceramic is also possible to maximise strength and simulate the appearance of natural teeth.
Dr.Parisha Patil,
BDS, MDS (Prosthodontist & Implantologist)
“Dr. Parisha Patil is a meticulous BDS, MDS (Prosthodontist & Implantologist) Certified Digital
Implantologist Cosmetic and Aesthetic Dentist, Geriatric Dentist, Maxillofacial Prosthodontist
Prize holder for 2 papers in National conferences Author of 3 publications”.
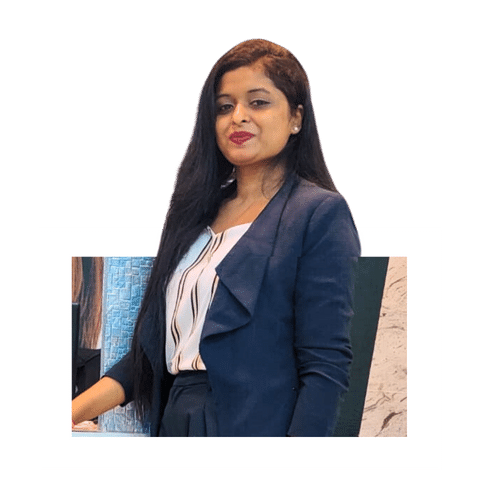

Firstly, a thorough clinical examination is conducted with radiographs, by the dentist. The suitability for crowns is assessed and any preparatory work is carried out. Your dentist will also be able to advise on material choices, treatment sequence and any other concerns you may have.
At the second appointment, the teeth to be crowned are prepared. This involves reduction of the tooth size (usually under local anaesthesia) followed by an impression or mould of the prepared tooth. This trimming of the tooth is required to create space for the crown to be fitted. The mould taken is then sent to a laboratory where skilled technicians will fabricate the crown. In the meantime, a temporary crown is made and fitted onto the trimmed tooth.
At the third appointment, the temporary crown is removed and the tooth surfaces cleaned. The completed crown is tried on the tooth for fit, harmony with the bite, and appearance. Finally, the crown is cemented onto the prepared tooth with dental cement.
Crowns are made of inert materials that do not deteriorate over time. However, the underlying tooth is still prone to decay and gum disease.
Ceramic on the surface may chip or fracture. Avoid chewing excessively-hard substances like ice or bones. Daily brushing and flossing are essential for maintaining good oral health as well as keeping the crown trouble-free. The most vulnerable portion of the crown is the margin or the junction between tooth and crown.
Regular check-ups will enable your dentist to detect any problems with your crown and recommend necessary treatment.
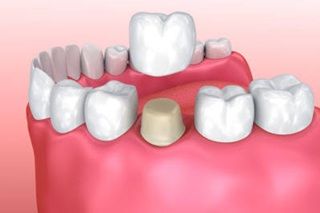
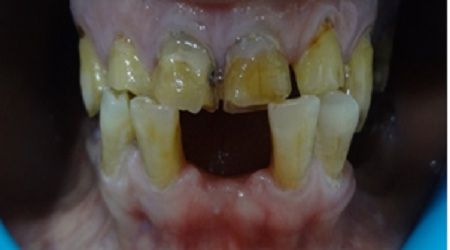
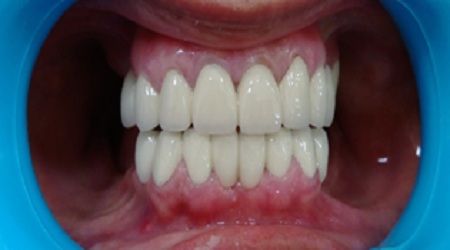
Crowns and bridges in dental terminology refers to a type of prosthesis that covers the tooth to protect it from decay or fracture or replaces the missing teeth so as to restore the form, function and aesthetics of the patient.
What is a dental crown ?
A dental crown is a cap or a cover used to enclose a natural tooth entirely to restore its shape, function and appearnace. it protects the tooth from further decay or fracture and in lot of cases it enhances the smile of the patient by correcting the shape, color and alignment of the front teeth.
A dental crown is bonded on the existing tooth abutment by a luting cement specially developed for this purpose. a crown is supposed to cover the tooth entirely and sit on the tooth portion right at the gum margin from all sides.
A bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants.Bridge is made up of more than 2 crowns . The number of missing teeth determine the number of abutments to be used. Basically the total root surface of the abutments used should be more than the root surface area of the missing teeth to be replaced. One of the major causes of bridge failure is the violation of this basic simple rule. The choice of material
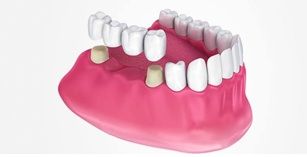
for bridge is also determined by our prosthodontist keeping the area of concern,the strength needed, patient's cost factor in mind.
Some important factors to be considered during crown/ bridge fabrication -
Margin- Supragingival/ Subgingival/ Equigingival. Supragingival margins are more biocompatible, hence used for posterior crowns. Subgingival are more esthetic, hence used mainly in anterior crowns. Equigingival margins are the most preferable as they are easy to maintain and esthetic as well. Finish lines could be chamfer, shoulder, feather edged depending on the material of prosthesis to be done.
Clearance and height- It is important to check the bite and have sufficient clearnace to fabricate a decent prosthesis. Crown lengthening procedure may be needed in some cases. our prosthodontists here at Haident measure and precisely trim off exactly the right amount of tooth structure so as to maintain adequate thickness for the crown and at rhe same time maintain the strength of the underlying tooth structure by not shaving off more tooth structure than what is needed
Occlusion- Occlusion plays the most important part in any restoration. It is mandatory to check the restoration in centric as well as eccentric occlusion before cementation. Canine guidance and incisal guidance should also be checked. This is where the expertise of our Prosthodontist shall come into play.
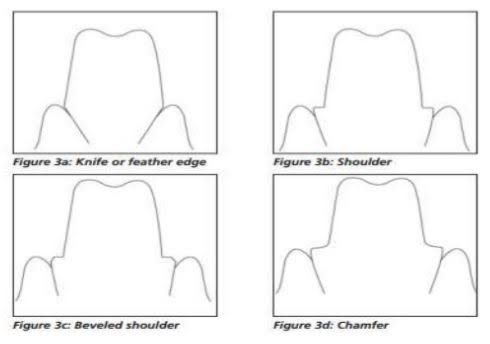
Clearance and height- It is important to check the bite and have sufficient clearnace to fabricate a decent prosthesis. Crown lengthening procedure may be needed in some cases. our prosthodontists here at Haident measure and precisely trim off exactly the right amount of tooth structure so as to maintain adequate thickness for the crown and at rhe same time maintain the strength of the underlying tooth structure by not shaving off more tooth structure than what is needed
Occlusion- Occlusion plays the most important part in any restoration. It is mandatory to check the restoration in centric as well as eccentric occlusion before cementation. Canine guidance and incisal guidance should also be checked. This is where the expertise of our Prosthodontist shall come into play.
Dental crowns are fabricated in the laboratory using different materials, like metal, Porcelain fused to metal, Zirconia, Emax, Tilite, acrylic.
Each material has its own pros and cons and depending on the site and purpose of restoration, our Prosthodontist at Haident decides which material would suit you the best.
Here is a brief of the commonly used crown/ bridge materials used in dentistry-
Metal crowns-
These are made of nickel chromium cobalt alloys . metal crowns are most economical and also one of the strongest options available. but difficult fabrication techniques, less precise fit and highly unaesthetic makes it a rarely used option in todays dentistry.
Porcelain fused to metal (PFM)-
these are the workhorses of modern dentistry.
This type of crown is basically a thin metal shell covered entirely with porcelain or ceramic compenent. it has very good strength that is more than adequate for normal healthy individual and it has reasonably good asthetics making it the material of choice for posterior or back teeth.

Tilite
this is very similar to PFM crowns. only difference is that the inner metal shell is made up of titanium alloy which makes it lighter stronger and also more precise fitting than PFM. it is also used in patients with known nickel allergy.
Zirconia
this is also called as all ceramic crown since it doesnt have any metal component in it. The inner shell is made up of zirconia or more precisely zirconium dioxide which is the hardest material available to make crowns.
Also it is available in any tooth shade that we want, making it a reasonably good aesthic option. It can be used in both anteior and posterior teeth making it the material of choice in today's modern dentistry.
Emax
Emax material is a glass like material made up of lithium di slicate. It is the most aesthetic option as it closely matches the human enamel in both colour and translucency. It is not as strong as zirconia but it is more aesthetic and natural looking than zirconia making it ideal for anterior teeth restorations.
The fabrication and delivery of crowns and bridges from the laboratory usually takes about a week's time and 2-3 sittings. We at Haident have the best doctors and tie ups with the finest labs in the country, making the same possible in a matter of 3-4 days approximately ( faster deliveries also possible in certain cases); without a compromise in the quality; hence making Haident the choice the clinic for patients across the globe.
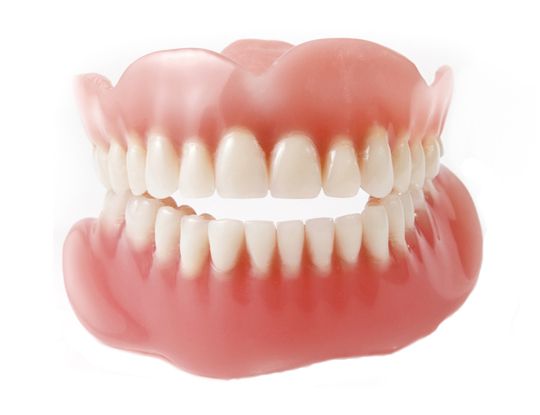
A denture is a removable prosthesis used to replace missing teeth. Commonly referred to as ‘false teeth’, a denture is usually made of acrylic or a combination of acrylic and metal. A partial denture is fitted to replace some missing teeth whilst a complete denture is indicated when all natural teeth are missing. A good set of dentures helps you to eat, speak, function, and often improves a person’s appearance.
Depending on the complexity of each case, the duration of the treatment will vary. After the initial visit of examination and diagnosis, the subsequent visits will include taking impressions of the mouth, bite registration, try-in of the denture, fitting and review.
New dentures always feel strange when first placed in your mouth. Several days or weeks will be required before you get accustomed to them. Adaptation varies with different persons and often time and experience are essential before dentures can be worn comfortably and function effectively.
Eating – Eating will take a little practice. Start with soft foods and foods cut into small pieces will help. Chew slowly using both sides of your mouth at the same time to prevent dentures from tipping. Once you become accustomed to chewing, include other foods until you return to your normal diet.
Increased salivary flow – You may experience an increase in salivary flow when the dentures are first inserted. This is a natural response of the salivary glands that will return to normal after a few weeks. You can improve the situation by swallowing more often.
Speech – New dentures may alter your speech initially. Pronouncing certain words may require practice. Reading out loud and repeating troublesome words will speed up the adaptation process. This problem rarely persists beyond two weeks.
Sore spots – Minor irritation caused by surface irregularities or pressure spots on the denture-bearing areas are quite common. Your dentist will relieve the discomfort by adjusting the denture surface. Stop wearing the denture if the irritation persists. Consult your dentist immediately.
Like natural teeth, dentures can accumulate plaque and food debris, particularly in areas where the denture is in contact with the remaining teeth and gum. In addition to the usual oral hygiene measures like tooth brushing, dentures should be cleaned regularly. Poor denture hygiene can result in stains on the denture and a bad odour.
If possible, dentures should be removed and cleaned after every meal. When cleaning, remember the following:
During the first few days you are advised to wear them most of the time except when sleeping. Always remove the dentures before going to bed. This will allow your gum tissues to rest and promote oral health. Gentle massaging of the gums with a soft toothbrush is encouraged. Remember to soak the dentures in water to prevent them from drying out.
Your jawbones and gums naturally shrink over time and this can cause the dentures to fit less securely. Ill-fitting dentures can give rise to chewing difficulties, soreness, infections and changes in facial support. It is important that you visit your dentist to have your dentures and oral tissues evaluated yearly. Your dentures may need to be adjusted, relieved or even relined from time to time to ensure an optimal fit. Do not attempt to adjust the denture yourself – seek professional help.
With time and practice you will soon learn to eat, talk and smile with your dentures as you would with your natural teeth.